Asphalt Base Course
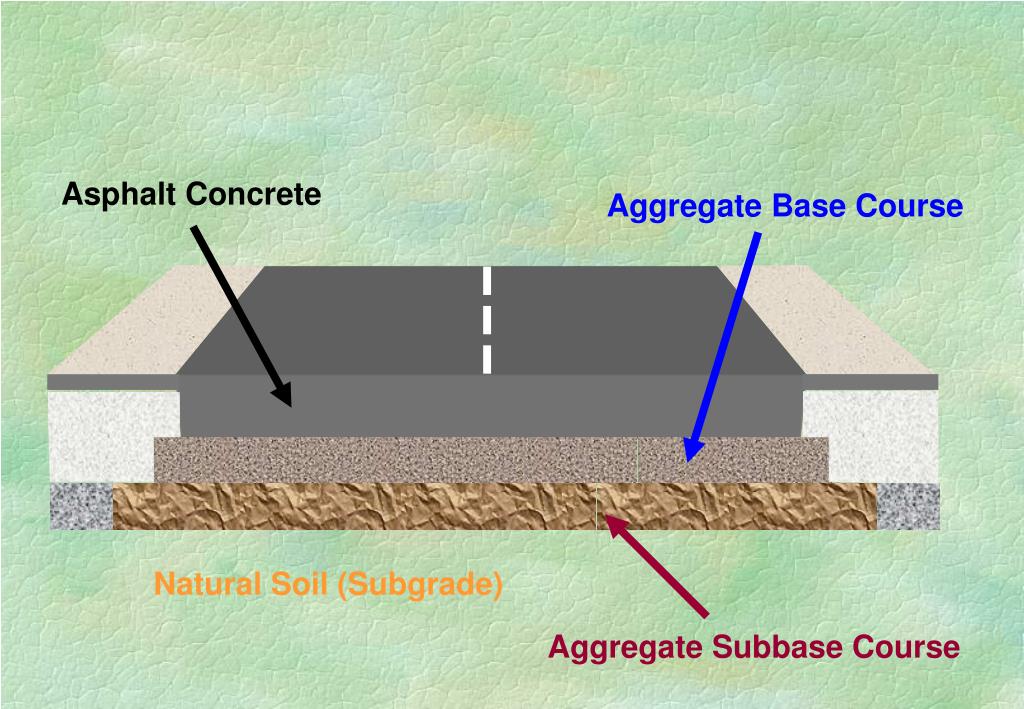
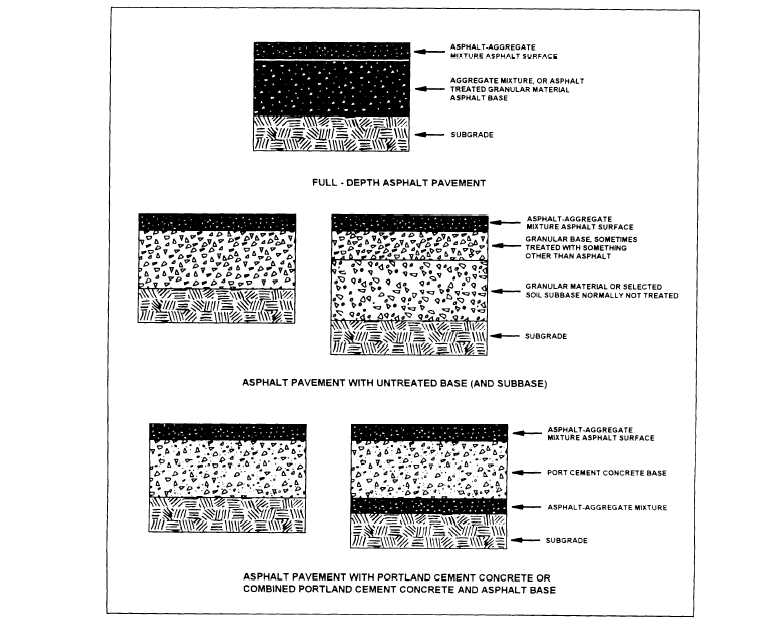
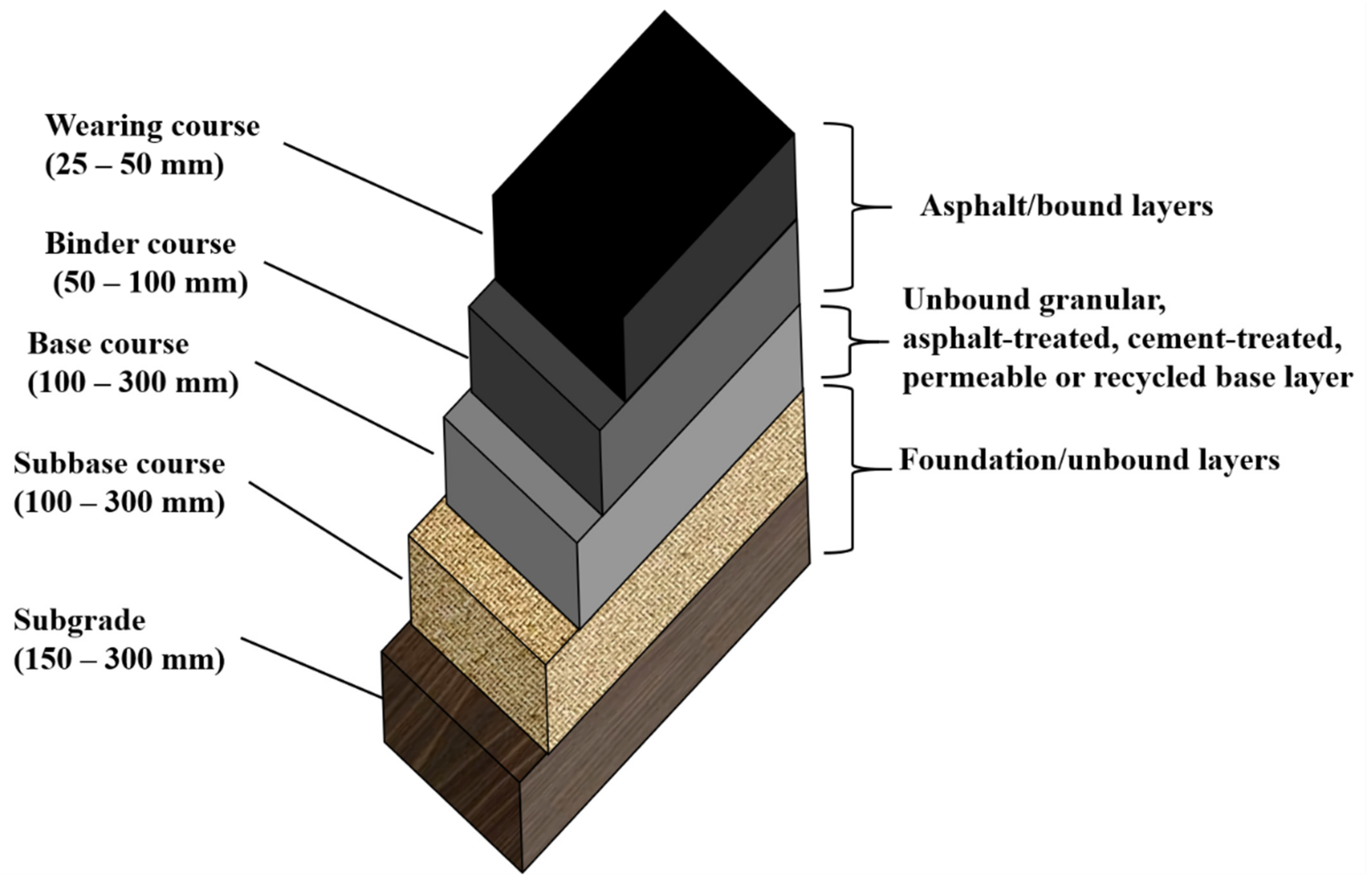
Asphalt Base Course - Road structure cross section is composed of the following components: Web the best option is aggregate base course, also known as“crusher run,” a mix of stone of every size from about 3/8 inch down to stone dust, so it knits together extremely well. The second layer is mostly called the binder course. A good base course should have enough strength and stiffness to guarantee the service performance of. The term asphalt concrete base is used in this manual to describe both hdot's hot mix asphalt base course (hmab course) and the county asphalt treated base (atb). The two main layers are the base course and the wearing course. What asphalt materials should be used for prime coats? This is the top layer, which consists of the pcc slab. It is typically made of a recipe of different sizes of aggregate rock inclusive of 1″ to fine dust. Asphaltenes are a byproduct of the deasphalting process of oil sand bitumen and have no significant value in the asphalt industry. What asphalt materials should be used for prime coats? The two main layers are the base course and the wearing course. Web the surface, binder, and base courses are typically different in composition and are placed in separate construction operations. Asphalt leveling course is defined as a layer of asphaltic concrete pavement of varying thickness spread on an existing pavement. For a prime coat to be effective it must be able to penetrate into the base course. This is the layer directly below the pcc layer and generally consists of aggregate or stabilized subgrade. This is the layer (or layers) under the base layer. Web the asphalt base course and wearing course represent the key asphalt layers in this system.. Web asphalt leveling course by jason brazer, p.e. This is the layer directly below the pcc layer and generally consists of aggregate or stabilized subgrade. A subbase is not always needed and therefore may often be omitted. Web in general the asphalt layers are paved on a bound or unbound road base layer. And that the subgrade must be composed. Web the best option is aggregate base course, also known as“crusher run,” a mix of stone of every size from about 3/8 inch down to stone dust, so it knits together extremely well. The term asphalt concrete base is used in this manual to describe both hdot's hot mix asphalt base course (hmab course) and the county asphalt treated base. For a prime coat to be effective it must be able to penetrate into the base course. Web kazmee, h, mishra, d & tutumluer, e 2015, sustainable alternatives in low volume road base course applications evaluated through accelerated pavement testing. Web asphalt leveling course by jason brazer, p.e. The thickness of the drainage layer can determined by the overall thickness. Starting at the road surface, the first layer is called the surface course. This is the layer (or layers) under the base layer. Web to provide adhesion between the base course and the succeeding course. Base courses are usually constructed out of crushed aggregate or hma. Web kazmee, h, mishra, d & tutumluer, e 2015, sustainable alternatives in low volume. Web the asphalt base course and wearing course represent the key asphalt layers in this system. Asphalt pavement is composed of multiple layers, each with a specific purpose. Web the surface, binder, and base courses are typically different in composition and are placed in separate construction operations. Asphaltenes are a byproduct of the deasphalting process of oil sand bitumen and. The pavement layers for two common methods, full depth hma and hma over aggregate base, of hma construction are shown in. Gsp 256, american society of civil engineers (asce), pp. The lower layers are the base courses. It is located under the surface layer consisting of the wearing course and sometimes an extra binder course. This is the layer directly. This is the top layer, which consists of the pcc slab. Web composition of road structure: Asphalt pavement is composed of multiple layers, each with a specific purpose. It provides additional load distribution and contributes to drainage. Web to provide adhesion between the base course and the succeeding course. Web the base course will bear the vertical loads that are transferred from the asphalt layer and will diffuse the loads into a subbase course or subgrade. The pavement layers for two common methods, full depth hma and hma over aggregate base, of hma construction are shown in. Web in general the asphalt layers are paved on a bound or. The pavement layers for two common methods, full depth hma and hma over aggregate base, of hma construction are shown in. Web to provide adhesion between the base course and the succeeding course. This is the top layer, which consists of the pcc slab. Asphaltenes are a byproduct of the deasphalting process of oil sand bitumen and have no significant value in the asphalt industry. If the permeable base is employed, the installation of drainage layer is not necessary. And that the subgrade must be composed of soil of such quality and be so prepared as to with stand, without failure, pressures of at least 11 psi. Web composition of road structure: Road structure cross section is composed of the following components: Web in general the asphalt layers are paved on a bound or unbound road base layer. A subbase is not always needed and therefore may often be omitted. Web asphalt base course and wearing course what you need to know asphalt is a common material used for paving roads, parking lots, driveways, and more. Surface/wearing course in pavement cross section: Web the best option is aggregate base course, also known as“crusher run,” a mix of stone of every size from about 3/8 inch down to stone dust, so it knits together extremely well. Web it is obvious that the base course must be constructed of material that is capable of withstanding pressures of 78 psi. The term asphalt concrete base is used in this manual to describe both hdot's hot mix asphalt base course (hmab course) and the county asphalt treated base (atb). This is the layer directly below the pcc layer and generally consists of aggregate or stabilized subgrade.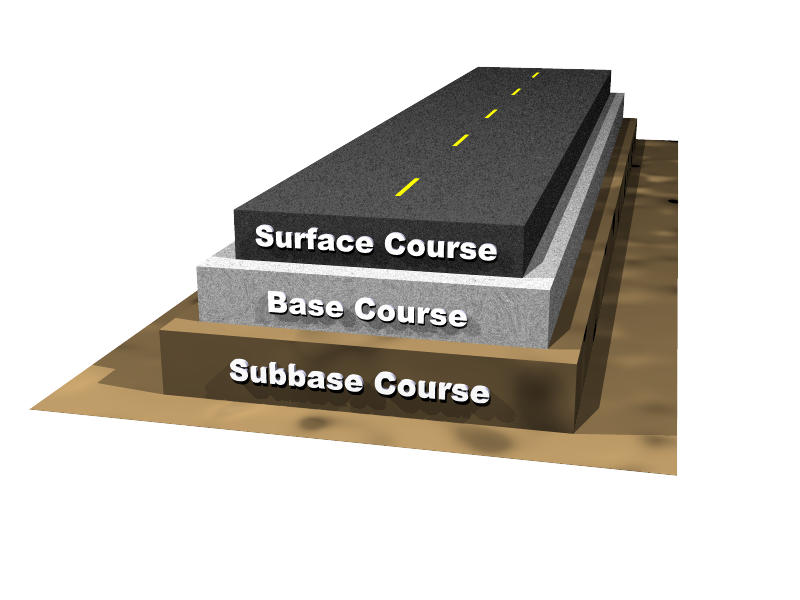
Pavement Interactive

AC 20mm Limestone Dense Builder Course Newlay Asphalt
PPT Introduction to Pavement Design Concepts PowerPoint Presentation

Gary Cooper Paving Cross section showing base course and wearing

Road Construction Process Asphalt Base Course at Site YouTube

Anatomy of Asphalt Pavement Eagle Rock
Function of Base Course and Subgrade

Asphalt Leveling Course
Application of RAP in Asphalt Concrete Pavements Encyclopedia MDPI

Aggregate Base Course laying on site ABC laying Road Construction
Web Asphalt Leveling Course By Jason Brazer, P.e.
Base Courses Are Usually Constructed Out Of Crushed Aggregate Or Hma.
“The Idea Is To Compact It So Well That It’s Watertight,” Mark Says.
The Top Layers Of Pavement Which Is In Direct Contact With The Wheel Of The Vehicle.
Related Post: