Buyer In Ordinary Course
Buyer In Ordinary Course - This course teaches how to value and price m&a deals and to choose the optimal financing mix for an m&a deal. (1) the initial contract date, (2) the identification date, or (3) the title date; A person that buys goods in good faith. An ordinary purchaser who acts in good faith, meaning honesty and fair dealing in the transaction and with no knowledge that the deal impairs the ownership or security rights of another, to buy goods from a seller who normally sells that kind of goods. Buyer in ordinary course of business means a person who in good faith and without knowledge that the sale to him is in violation of Or (2) 45 days after the purchase. As such, the buyers knowledge that a security interest exists is irrelevant. Web except as otherwise provided in subsection (e), a buyer of goods other than a buyer in ordinary course of business takes free of a security interest to the extent that it secures advances made after the earlier of: I got a call the other day from a buyer. Web a “buyer in the ordinary course of business” is a person who, in good faith and without knowledge that the sale to the buyer is in violation of the ownership rights or security interest of a third party in the goods, buys in ordinary course from a person in the business of selling goods of that kind. Web this course focuses on the theory and practice of mergers and acquisitions (m&a), with a focus on the finance. This may provide the ability to “bypass” an undesired impact of §1231 capital gains tax treatment of the standing crops and allow the farmer to report the value of the crops as ordinary income while preserving the ability to deduct. She was concerned with the lack of inventory, and was. rebecca west on instagram: The course focuses on all the major types of m&a deals including strategic m&a, private equity leveraged buyouts (lbos), and restructuring deals such as spinoffs and asset transfers. Or (2) 45 days after the purchase. Web this course focuses on the theory and practice of mergers. Web (9) buyer in ordinary course of business means a person that buys goods in good faith, without knowledge that the sale violates the rights of another person in the goods, and in the ordinary course from a person, other than a pawnbroker,. Web except as otherwise provided in subsection (e), a buyer of goods other than a buyer in. Web the most often applied alternatives for determining the point at which a buyer achieves ordinary course status include: The course focuses on all the major types of m&a deals including strategic m&a, private equity leveraged buyouts (lbos), and restructuring deals such as spinoffs and asset transfers. She was concerned with the lack of inventory, and was. rebecca west on. Web there are 5 modules in this course. Web (a) [buyer in ordinary course of business.] except as otherwise provided in subsection (e), a buyer in ordinary course of business, other than a person buying farm products from a person engaged in farming operations , takes free of a security interest created by the buyer's seller, even if the security. Web a buyer in the ordinary course of business will prevail over a secured creditor. Buyer in ordinary course of business means a person who in good faith and without knowledge that the sale to him is in violation of The course focuses on the relevant provisions of subchapters s and k of the internal revenue code, as well as. This is true whether the security interest is perfected or no. In particular, we will learn to value and price m&a deals and how to choose the optimal financing mix. Without knowledge that the sale violates the rights of another person in the goods. I got a call the other day from a buyer. This may provide the ability to. Web (a) buyer in ordinary course of business means a person who in good faith and without knowledge that the sale to him [or her] is in violation of the ownership rights or security interest or leasehold interest of a third party in the goods, buys in ordinary course from a person in the business of selling goods of that. She was concerned with the lack of inventory, and was. rebecca west on instagram: Web (a) [buyer in ordinary course of business.] except as otherwise provided in subsection (e), a buyer in ordinary course of business, other than a person buying farm products from a person engaged in farming operations , takes free of a security interest created by the. The finance of m&a uses tools from different areas of finance to help managers and investment bankers design successful m&a deals. In the ordinary course from a person, other than a pawnbroker, in the business of selling goods of that. As such, the buyers knowledge that a security interest exists is irrelevant. Without knowledge that the sale violates the rights. Web the most often applied alternatives for determining the point at which a buyer achieves ordinary course status include: As such, the buyers knowledge that a security interest exists is irrelevant. Web the buyer where the farmer reserves the right to harvest and sell the standing crop. This course teaches how to value and price m&a deals and to choose the optimal financing mix for an m&a deal. An ordinary purchaser who acts in good faith, meaning honesty and fair dealing in the transaction and with no knowledge that the deal impairs the ownership or security rights of another, to buy goods from a seller who normally sells that kind of goods. The course focuses on the relevant provisions of subchapters s and k of the internal revenue code, as well as related. Web there are 5 modules in this course. This is true whether the security interest is perfected or no. I got a call the other day from a buyer. (1) the term “buyer in the ordinary course of business” means a person who, in the ordinary course of business, buys farm products from a person engaged in farming operations who is in the business of selling farm products. The meaning of buyer in ordinary course of business is a bona fide purchaser who in a normal or regular business procedure buys goods from a seller in the business of selling goods of that kind. Web (a) [buyer in ordinary course of business.] except as otherwise provided in subsection (e), a buyer in ordinary course of business, other than a person buying farm products from a person engaged in farming operations , takes free of a security interest created by the buyer's seller, even if the security interest is perfected and the buyer knows. A person that buys goods in good faith. Web (a) buyer in ordinary course of business means a person who in good faith and without knowledge that the sale to him [or her] is in violation of the ownership rights or security interest or leasehold interest of a third party in the goods, buys in ordinary course from a person in the business of selling goods of that kind but does not includ. The course focuses on all the major types of m&a deals including strategic m&a, private equity leveraged buyouts (lbos), and restructuring deals such as spinoffs and asset transfers. The finance of m&a uses tools from different areas of finance to help managers and investment bankers design successful m&a deals.
Buyers Agent Courses Upskill From Real Estate Sales

Understanding Different Buyer Types Infographic MTD Sales Training

25+ Completely FREE Marketing Courses For Bloggers And Entrepreneurs

Understanding The Buyer Grant Cardone Sales Training University

Sales Training Selling To Different Buyer Types North & Western
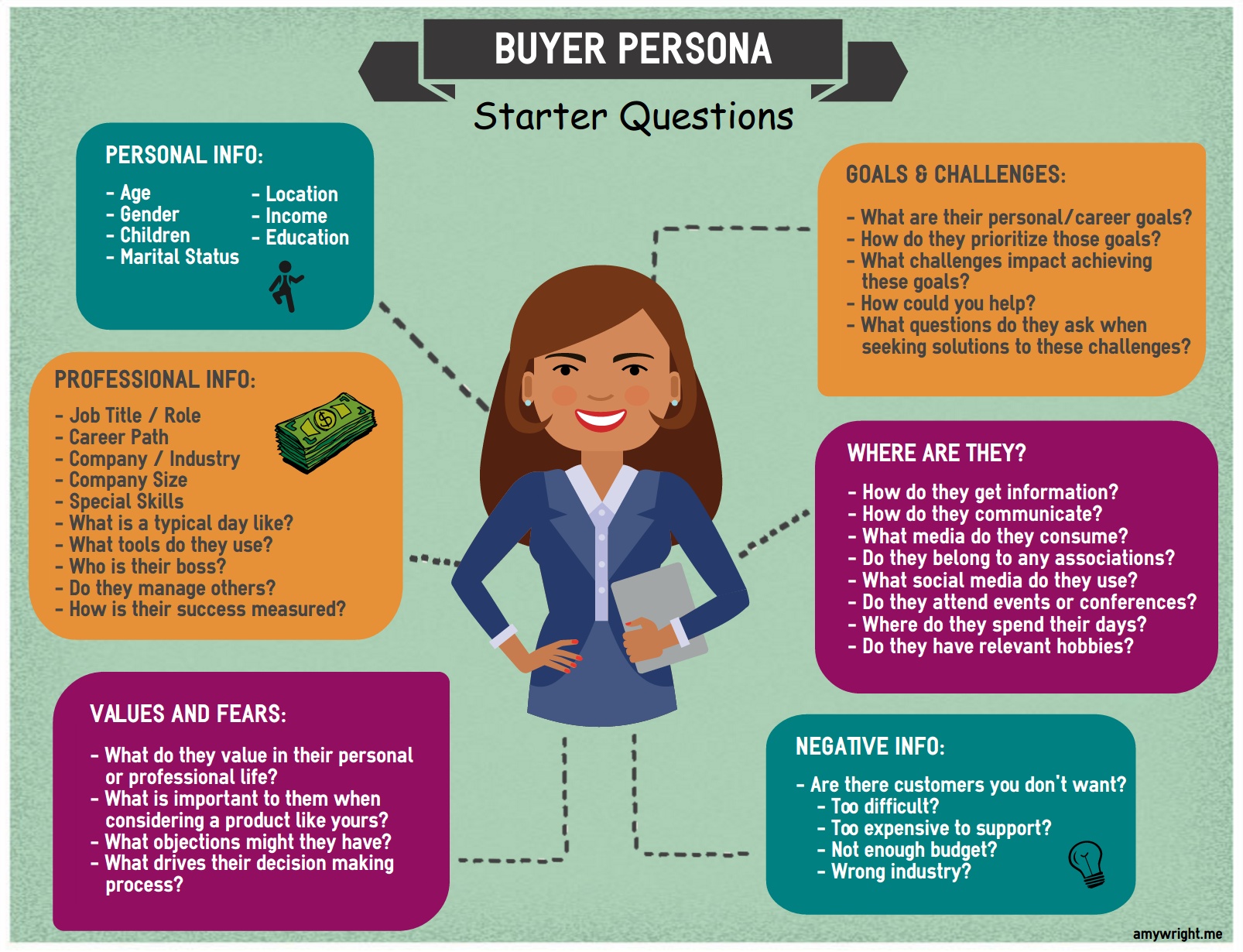
Creating A 5Star Buyer Persona For Your Kickass Business

Bargaining Power of Buyers & Suppliers Explained Marketing91
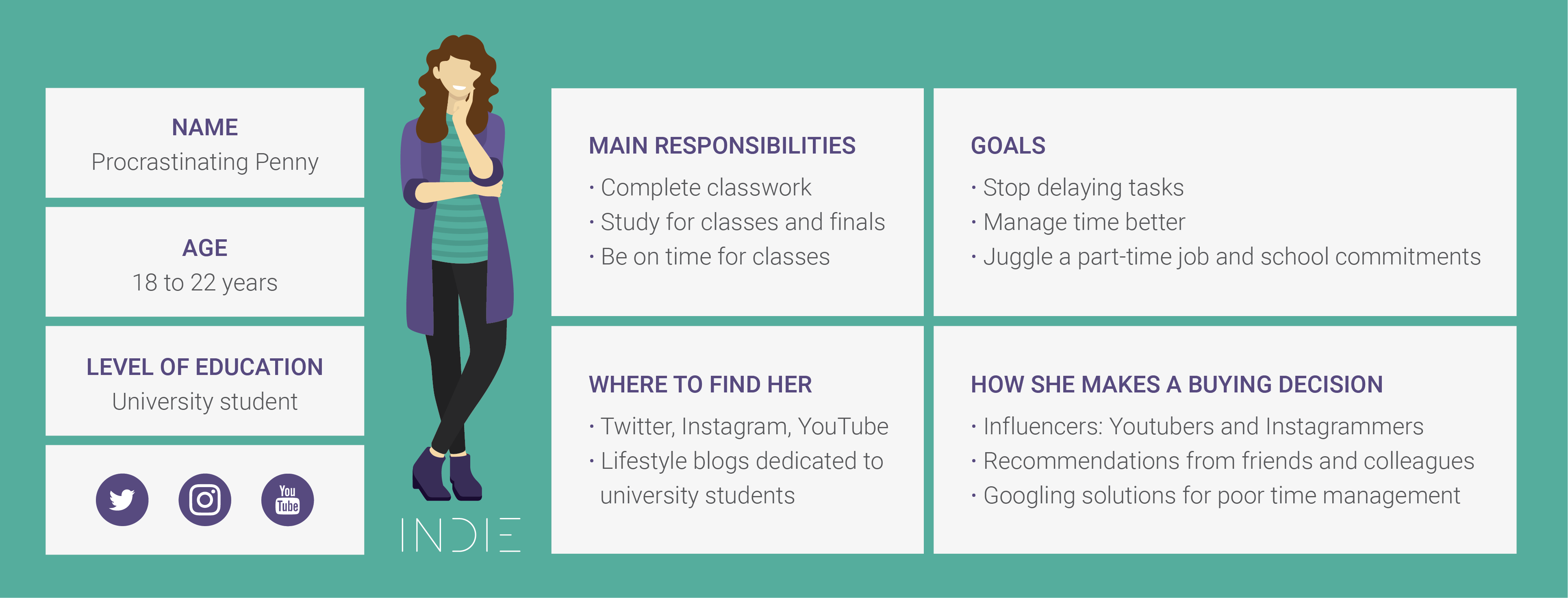
The entrepreneur’s guide to buyer personas for online courses [Part 1
Buyers Bargaining Power Porters Five Forces Analysis

PPT Chapter 35 Secured Transactions in Personal Property PowerPoint
Web (9) Buyer In Ordinary Course Of Business Means A Person That Buys Goods In Good Faith, Without Knowledge That The Sale Violates The Rights Of Another Person In The Goods, And In The Ordinary Course From A Person, Other Than A Pawnbroker,.
Buyer In Ordinary Course Of Business Means A Person Who In Good Faith And Without Knowledge That The Sale To Him Is In Violation Of
Web A Buyer In The Ordinary Course Of Business Will Prevail Over A Secured Creditor.
Web § 205.212 “Buyer In Ordinary Course Of Business” And “Security Interest.” The Terms “Buyer In Ordinary Course Of Business” And “Security Interest” Are Defined In Subsections (C) (1) And (7).
Related Post: